The emergence of smart cities and Industry 4.0 – A platform for future generation
Smart city is a newly developed concept and the term had arisen during 2008 when the world was facing tremendous economical crisis. By following this concept, it is possible to develop a sustainable replica for the cities and an excellence of life can be created for the dwellers. Smart city is not only related to technical discipline but also involves various managerial, financial, civilized and lawful features. Major dimensions of smart cities are smart people, smart environment, smart government, smart mobility and smart economy (Figure 1). Disruption has redefined the role of leaders today and mere personal charisma will not make them as successful leaders. Rapid changes in digital technology is influencing and transforming the entire society. The digital age and its impact has created new challenges and it demands changes in even reshaping leadership. Instead of viewing technological advancement as threat, it is good to look for the opportunities they bring to the society. They need to add new skills along with the traditional skills. Hence digital leadership is needed to deal with digital disruption successfully. Digital leaders should keep up with global revolution and have an open attitude to incorporate changes. They should have a thirst for knowledge and should respond to immediate changes which can happen when they widen their networks.

Figure 1 – Dimensions of Smart Cities
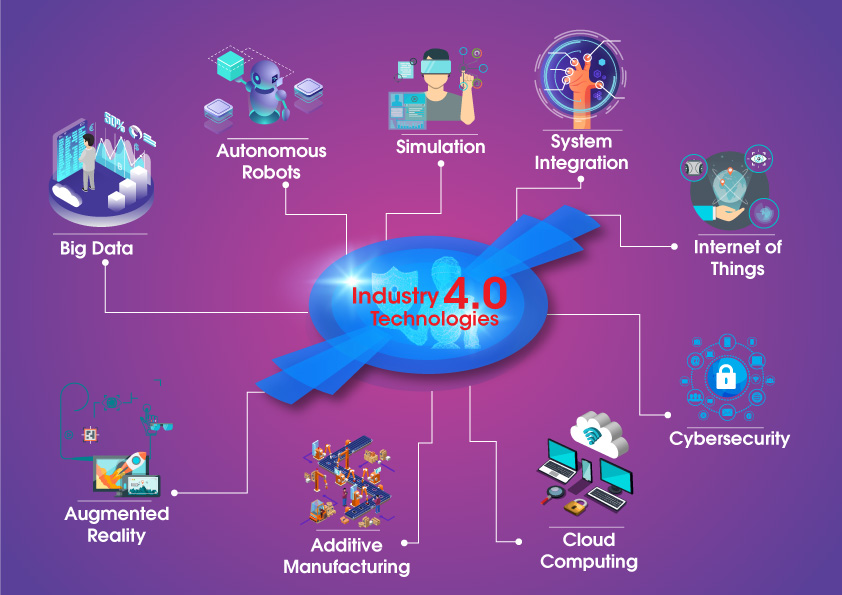
Figure 2 – Industry 4.0 technologies
Industry 4.0 helps to develop smart products. Industry 4.0 refers to smart industrialized initiatives and better known as a place where new products and technologies are manufactured, whereas smart city is a podium where these products and technologies get deployed. Industry 4.0 creates a flexible, adaptive, smart platform for disruptive transformation and helps to maintain citizens value outcomes, sustainable financial expansion and better societal commitment. Figure 2 shows the Industry 4.0 technologies. Internet of Things (IoT) – a key technology of Industry 4.0 may be the success factor of smart cities that can improve the fluctuation of data or the efficiency of crisis responses. The IoT is a network of physically linked machines i.e. vehicles, robotic co-ordinations and infrastructures, which can allow these things to join and exchange information. Another key features of Industry 4.0 are Internet of Services (IoS)- which can enable particularly smart transportation and logistics; whereas Internet of Energy (IoE) helps in proper consumption of natural resources. Artificial intelligence(AI)- is intelligence exhibited by machines in contrast to intelligence demonstrated by human-beings which has become a vital part of technology industry.
Thus, the connectivity of smart city and Industry 4.0 may create huge opportunities to join the physical and the digital world and it can develop the public and private sector’s effectiveness, expand financial benefits and improve the standard of living. Hence for the expansion of smart cities, sufficient investment is required in the businesses that strive to facilitate the 4th industrial uprising through Artificial Intelligence (AI), IoT and advanced network exposure. This includes 5G coverage, edge and connectivity that can maintain thousands of smart and digital cities sensing devices. IoT, IoS, IoE and other technologies like cyber security, big data, simulation, robotics, augmented reality, additive manufacturing, system integration and cloud computing may act as a center which can build a bond between Smart City Ideas and Industry 4.0-where Industry 4.0 can act as a component of smart city. When production-based Industry 4.0 is linked with smart transportation structures of the smart city through connected information, then it is possible to build very efficient, demand-based and advanced production based manufacturing companies Impact of these technological advancements are particularly needed for developing and underdeveloped countries to improve the living standards of the people.

Associate Professor in Digital Cities, MMU.

